Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 by ion beam breeding technology
by ion beam breeding technologySato, Katsuya; Ueda, Ryoshiro*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issey*; Ono, Yutaka
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 100, 2016/02

Ueda, Ryoshiro*; Sato, Katsuya; Hayashi, Hidenori*; Narumi, Issey*; Ono, Yutaka
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 101, 2016/02
Sato, Katsuya; Ueda, Ryoshiro; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issey*; Ono, Yutaka
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 117, 2015/03

Ueda, Ryoshiro; Sato, Katsuya; Hayashi, Hidenori*; Narumi, Issey*; Ono, Yutaka
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 118, 2015/03
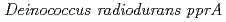 gene
geneOba, Hirofumi*; Sato, Katsuya*; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Narumi, Issei
Gene, 363, p.133 - 141, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:55.59(Genetics & Heredity)Three transcriptional start points for the 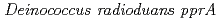 were located at positions -156, -154 and -22 upstream from the
were located at positions -156, -154 and -22 upstream from the  translation initiation site. The amount of the three extended products increased in cells exposed to 2-kGy followed by a 0.5-h post-incubation, suggesting the existence of at least two radiation responsive promoters for
translation initiation site. The amount of the three extended products increased in cells exposed to 2-kGy followed by a 0.5-h post-incubation, suggesting the existence of at least two radiation responsive promoters for  expression. A luciferase reporter assay revealed that the distal promoter is located between positions -208 and -156 from the translation initiation site, while the proximal promoter is located between positions -57 and -22. The region located between positions -57 and -38 was indispensable for proximal promoter activity. Site-directed mutagenesis of a thymine positioned at -33 resulted in severe impairment of promoter activity, and suggested that the thymine functions as a master base for the proximal radiation responsive promoter. The results also suggested that up-regulation of
expression. A luciferase reporter assay revealed that the distal promoter is located between positions -208 and -156 from the translation initiation site, while the proximal promoter is located between positions -57 and -22. The region located between positions -57 and -38 was indispensable for proximal promoter activity. Site-directed mutagenesis of a thymine positioned at -33 resulted in severe impairment of promoter activity, and suggested that the thymine functions as a master base for the proximal radiation responsive promoter. The results also suggested that up-regulation of  expression by the
expression by the  gene product is triggered at the promoter level.
gene product is triggered at the promoter level.
 ,
,  or
or 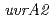 gene product for UV resistance in
gene product for UV resistance in 
Tanaka, Masashi*; Narumi, Issei; Funayama, Tomoo; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Watanabe, Hiroshi*; Matsunaga, Tsukasa*; Nikaido, Osamu*; Yamamoto, Kazuo*
Journal of Bacteriology, 187(11), p.3693 - 3697, 2005/06
Times Cited Count:47 Percentile:62.15(Microbiology)no abstracts in English

Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Narumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Kitayama, Shigeru; Watanabe, Hiroshi*
Uchu Seibutsu Kagaku, 18(3), p.134 - 135, 2004/11
no abstracts in English
 that stimulates DNA ligation
that stimulates DNA ligationNarumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; Cui, S.*; Funayama, Tomoo; Kitayama, Shigeru; Watanabe, Hiroshi*
Molecular Microbiology, 54(1), p.278 - 285, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:133 Percentile:91.37(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)The extraordinary radiation resistance of  results from the efficient capacity of the bacterium to repair DNA double-strand breaks. By analyzing the DNA damage repair-deficient mutant, KH311, a unique radiation-inducible gene (designated
results from the efficient capacity of the bacterium to repair DNA double-strand breaks. By analyzing the DNA damage repair-deficient mutant, KH311, a unique radiation-inducible gene (designated  ) responsible for loss of radiation resistance was identified. Investigations in vitro showed that the gene product of
) responsible for loss of radiation resistance was identified. Investigations in vitro showed that the gene product of  (PprA) preferentially bound to double-stranded DNA carrying strand breaks, inhibited
(PprA) preferentially bound to double-stranded DNA carrying strand breaks, inhibited  exonuclease III activity, and stimulated the DNA end-joining reaction catalyzed by ATP-dependent and NAD-dependent DNA ligases. These results suggest that
exonuclease III activity, and stimulated the DNA end-joining reaction catalyzed by ATP-dependent and NAD-dependent DNA ligases. These results suggest that  has a radiation-induced nonhomologous end-joining repair mechanism in which PprA plays a critical role.
has a radiation-induced nonhomologous end-joining repair mechanism in which PprA plays a critical role.
 in the radioresistant bacterium
in the radioresistant bacterium 
Islam, M. S.*; Hua, Y.*; Oba, Hirofumi; Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Narumi, Issei
Genes and Genetic Systems, 78(5), p.319 - 327, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:27.54(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)no abstracts in English

Battista, J. R.*; Cox, M. M.*; Daly, M. J.*; Narumi, Issei; Radman, M.*; Sommer, S.*
Science, 302(24), p.567 - 568, 2003/10
no abstracts in English

Narumi, Issei
Hoshasen To Chikyu Kankyo; Seitaikei Eno Eikyo O Kangaeru, p.113 - 122, 2003/09
no abstracts in English
Narumi, Issei
Iden, 57(5), p.57 - 62, 2003/09
no abstracts in English
Narumi, Issei
Trends in Microbiology, 11(9), p.422 - 425, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:89.95(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)no abstracts in English

Hua, Y.*; Narumi, Issei; Gao, G.*; Tian, B.*; Sato, Katsuya; Kitayama, Shigeru; Shen, B.*
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 306(2), p.354 - 360, 2003/06
Times Cited Count:152 Percentile:95.76(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)We have identified a unique deinococcal gene,  , as a general switch for downstream DNA repair and protection pathways, from a natural mutant, in which
, as a general switch for downstream DNA repair and protection pathways, from a natural mutant, in which  is disrupted by a transposon. Complete functional disruption of the gene in wild-type leads to dramatic sensitivity to ionizing radiation. Radioresistance of the disruptant could be fully restored by complementation with
is disrupted by a transposon. Complete functional disruption of the gene in wild-type leads to dramatic sensitivity to ionizing radiation. Radioresistance of the disruptant could be fully restored by complementation with  . In response to radiation stress, PprI can significantly and specifically induce the gene expression of
. In response to radiation stress, PprI can significantly and specifically induce the gene expression of  and
and  and enhance the enzyme activities of catalases. These results strongly suggest that PprI plays a crucial role in regulating multiple DNA repair and protection pathways in response to radiation stress.
and enhance the enzyme activities of catalases. These results strongly suggest that PprI plays a crucial role in regulating multiple DNA repair and protection pathways in response to radiation stress.
Narumi, Issei
Science & Technology Journal, 12(5), p.50 - 51, 2003/05
no abstracts in English
 UV-endonuclease
UV-endonuclease 
Kitayama, Shigeru; Narumi, Issei; Funayama, Tomoo; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Bioscience Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 67(3), p.613 - 616, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.16(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)no abstracts in English
 and/or
and/or  in the extremely radioresistant bacterium
in the extremely radioresistant bacterium 
Nashida, Hiromi*; Narumi, Issei
Microbiology, 148(9), p.2911 - 2914, 2002/09
The extremely radioresistant bacterium  has the related homologous genes to bacterial lysine biosyntheses both through the aminoadipate pathway and the diaminopimelate pathway. We disrupted
has the related homologous genes to bacterial lysine biosyntheses both through the aminoadipate pathway and the diaminopimelate pathway. We disrupted  and/or
and/or  . The
. The  is homologous to
is homologous to  that is essential for the aminoadipate pathway. The
that is essential for the aminoadipate pathway. The  is homologous to
is homologous to  that is essential for the diaminopimelate pathway. Each disruptant of
that is essential for the diaminopimelate pathway. Each disruptant of  ,
,  , and
, and  and
and  grew in a minimal medium, as well as wild-type. This result shows that
grew in a minimal medium, as well as wild-type. This result shows that  employs a unique way for lysine biosynthesis.
employs a unique way for lysine biosynthesis.
Narumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro
JAERI-Conf 2002-005, p.158 - 171, 2002/03
 is characterized by its extraordinary resistance to the lethal and mutagenic effects of ionizing and ultraviolet irradiations and many other DNA-damaging agents. By analyzing a DNA repair-deficient mutant strain, we discovered that a novel protein participates in the extreme radiation resistance of
is characterized by its extraordinary resistance to the lethal and mutagenic effects of ionizing and ultraviolet irradiations and many other DNA-damaging agents. By analyzing a DNA repair-deficient mutant strain, we discovered that a novel protein participates in the extreme radiation resistance of  . The protein (designated PprA for promoting prominent repair) can recognize DNA strand breaks. Further, PprA would protect irradiation-damaged DNA from exonuclease activity and consequent degradation and thereby ensure DNA repair processes could function. Beside DNA-binding ability, PprA can promote the activities of DNA ligase and RecA, suggesting that PprA functions as a DNA repair-promoting protein to potentiate the effectiveness of DNA repair. These properties enable PprA to use the widespread application
. The protein (designated PprA for promoting prominent repair) can recognize DNA strand breaks. Further, PprA would protect irradiation-damaged DNA from exonuclease activity and consequent degradation and thereby ensure DNA repair processes could function. Beside DNA-binding ability, PprA can promote the activities of DNA ligase and RecA, suggesting that PprA functions as a DNA repair-promoting protein to potentiate the effectiveness of DNA repair. These properties enable PprA to use the widespread application  and
and  .
.

Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Narumi, Issei
JAERI-Conf 2002-005, p.172 - 184, 2002/03
 a DNA damage response mechanism. However, the damage response is poorly understood in
a DNA damage response mechanism. However, the damage response is poorly understood in  . By investigating the function of deinococcal proteins, we found that, unlike in
. By investigating the function of deinococcal proteins, we found that, unlike in  , LexA is not involved in the regulation of RecA in
, LexA is not involved in the regulation of RecA in  . This, in turn, led us to speculate that
. This, in turn, led us to speculate that  has an alternative DNA damage response mechanism with which to control
has an alternative DNA damage response mechanism with which to control  expression. Recently, we discovered that a novel protein regulates the expression of
expression. Recently, we discovered that a novel protein regulates the expression of  gene. The novel regulatory protein (designated as PprI) also control the induction of
gene. The novel regulatory protein (designated as PprI) also control the induction of  gene following
gene following  irradiation. Thus,
irradiation. Thus,  possesses unique mechanisms of DNA damage recognition and repair gene induction.
possesses unique mechanisms of DNA damage recognition and repair gene induction.
 by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis
by pulsed-field gel electrophoresisKikuchi, Masahiro; Narumi, Issei; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAERI-Conf 2002-005, P. 185, 2002/03
The most striking feature of the radioresistant bacterium  is that it can mend over 100 double-strand breaks of genomic DNA during post-irradiation incubation. This process can be clearly visualized using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). By a combination of protein synthesis inhibition treatment and PFGE analysis, it was possible to estimate an initial period required for induction of DNA repair proteins (induction time) and a total period required for completing DNA repair (repair time). PFGE is a powerful tool to analyze DNA damage and its repair process.
is that it can mend over 100 double-strand breaks of genomic DNA during post-irradiation incubation. This process can be clearly visualized using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). By a combination of protein synthesis inhibition treatment and PFGE analysis, it was possible to estimate an initial period required for induction of DNA repair proteins (induction time) and a total period required for completing DNA repair (repair time). PFGE is a powerful tool to analyze DNA damage and its repair process.